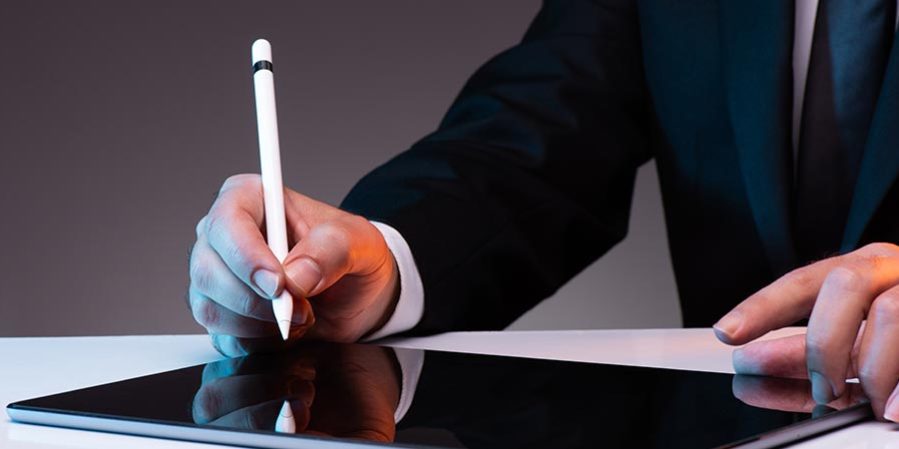
Issued only by a Certified Authority, a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) is a digital key that authorizes the identity of businesses and individuals holding the certificate. To get the DSC, there is a necessity to submit a duly-filled digital signature form. The digital signature certificate comprises information such as the name of the user, email address, country, the date on which the certificate was issued and the name of the certifying authority’s name. The authorization of the digital key takes place to assure the security and authenticity of documents filed online.
It is being observed that data tampering and forgery have been rapidly increasing in the businesses that revolve around manual paperwork. Due to the increase in the loss of important data, it has become a necessity to secure any data shared online and this lays emphasis on the use of Digital Signatures. The ability to authenticate a file, document or software has brought Digital Signatures into the limelight.
Paperwork replaced with Digital Signatures brings in a lot of benefits such as speed up document delivery, lessens operating costs and saves time & efforts.
Let’s take a look at how does Digital Signatures Work?
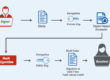
- On clicking sign, individuals create a unique digital fingerprint (known as hash) of the document through the use of the mathematical algorithm. The hash is precisely for this particular document; even the minor change made would serve a different hash as an outcome.
- On clicking sign, individuals create a unique digital fingerprint (known as hash) of the document through the use of the mathematical algorithm. The hash is precisely for this particular document; even the minor change made would serve a different hash as an outcome.
- On clicking sign, individuals create a unique digital fingerprint (known as hash) of the document through the use of the mathematical algorithm. The hash is precisely for this particular document; even the minor change made would serve a different hash as an outcome.
On verifying the Signature:
- When the document is opened in a digital signature-capable program like Microsoft Office, Adobe Reader, etc., the signer’s public key (already included in the digital signature) gets automatically used by the program for decryption of the document hash.
- For the document, a new hash is calculated through the program. If the new hash created gets matched with the decrypted hash from Step 1, it states that there is no alteration in the document and also displays the message ” No modification has been made since the signature was applied “.
The public key used in the signature is validated by the program to ensure that it belongs to the signer and displays the name of the signer.